The recent significant advancements in the field of artificial intelligence have laid a robust foundation for the emergence and strong development of AI Agents – intelligent systems that surpass traditional chatbots or conventional AI. AI Agents not only understand and respond but also possess the capability to autonomously plan, make decisions, and execute complex tasks. In the context of the profound digital transformation underway globally, the role of AI Agents is becoming increasingly crucial, ushering in a new and promising chapter for businesses and individuals alike. This article will explore the burgeoning growth, potential, and profound impacts that AI Agents are currently delivering and will continue to bring.
1. What are AI Agents and why do they matter?

AI Agents, also known as intelligent agents, are intelligent systems capable of performing tasks independently, flexibly, and efficiently without constant human intervention. They possess four core characteristics: autonomy – the ability to make decisions independently; reactivity – the capacity to recognize and adapt promptly to changes in the environment; proactiveness – not only reacting but also actively pursuing goals; and learning – improving performance through experience and new data.
Unlike conventional chatbots, which primarily focus on maintaining conversations based on pre-defined scripts, AI Agents can autonomously formulate plans, devise strategies, and handle a wide array of complex tasks beyond the scope of dialogue. Compared to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) – ideal systems capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can – current AI Agents have a narrower scope of application but are highly specialized and optimized within specific domains.
A simple illustration of how an AI Agent operates: Imagine you have an AI assistant for project management. Upon receiving a request to organize a meeting with multiple stakeholders, the AI Agent will automatically check the schedules of all members, identify the most suitable time slot, schedule the meeting, send out invitations, and even prepare necessary documents beforehand based on the meeting agenda – all executed proactively and swiftly without you having to issue step-by-step commands.
The Significance of AI Agents in the Era of Digital Transformation:
- Solving complex problems and automating multi-step processes.
- Enhancing work efficiency and productivity.
- Personalizing user experiences at a higher level.
- Unlocking new business models and services.
- Supporting data-driven decision-making and insightful analysis.
2. Types of AI Agents and potential applications
2.1 Classification of AI Agents

AI Agents can be categorized based on various criteria, including their operational architecture, reasoning capabilities, or application domain. Based on architecture and complexity, AI Agents can be broadly classified into five fundamental groups:
Reflex Agents: These represent the most basic type of AI Agent, operating on a direct response principle to the environment based on simple condition-action rules ("if-then"). They do not store historical or current environmental information, making them suitable primarily for predictable tasks.
Model-based Reflex Agents: An advancement over simple reflex agents, this group constructs an internal model of the world to understand the current state. This enables them to handle more complex situations, even when not all information is immediately available.
Goal-based Agents: These agents not only react to their environment but also leverage specific goals to make decisions. They possess the capability for planning and evaluating different actions based on which action will most effectively lead to the defined objective.
Utility-based Agents: Beyond pursuing goals, these agents optimize the level of "satisfaction" or "utility" of the achieved outcome, utilizing a utility function. This allows them to make decisions in scenarios with multiple seemingly rational options.
Learning Agents: This type of agent possesses the ability to self-improve over time by learning from experience. Learning Agents can modify their behavior based on feedback from the environment, enabling them to adapt more effectively to novel or changing situations.
This classification provides a clearer understanding of how different AI Agents operate and facilitates the selection of the appropriate model for specific application objectives, ranging from simple process automation to supporting strategic decision-making within enterprises.
2.2 Potential applications of AI Agents across industries
Enterprise
AI Agents are transforming business operations through intelligent automation and data-driven decision-making:
- Project Management: AI Agents can plan tasks, allocate resources, monitor progress, and automatically trigger alerts for potential delays.
- Business Process Automation (BPA): Repetitive tasks such as data entry, email correspondence, and inventory management can be efficiently and accurately handled by AI, surpassing human capabilities.
- Strategic Decision Support: By analyzing market trends, customer behavior, and internal performance, AI provides strategic recommendations for business leadership.
- Supply Chain Management: Demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and agile transportation coordination are enhanced through AI Agents capable of processing real-time data.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, AI Agents support clinicians and patients while enhancing personalized treatment capabilities:
- Diagnostic Assistance: AI can analyze medical imaging (CT, MRI), symptoms, and patient history to aid physicians in faster and more accurate diagnoses.
- Patient Record Management: AI Agents facilitate the collection, organization, and updating of patient records, thereby supporting more effective clinical decision-making.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates the research and development of new pharmaceuticals by simulating biological responses and predicting potential efficacy and toxicity.
- Virtual Patient Assistants: Providing medication reminders, addressing basic symptom inquiries, and monitoring health metrics remotely.
Education
AI Agents can personalize the learning experience, optimize teaching methodologies, and streamline classroom management:
- Personalized Virtual Tutoring: AI monitors individual learning progress and adapts content accordingly, leading to improved academic outcomes.
- Automated Grading: Systems can evaluate essays, multiple-choice tests, and provide feedback based on academic criteria.
- Intelligent Classroom Management: Analyzing student engagement, automating attendance, and supporting educators in developing tailored lesson plans.
Finance
AI Agents contribute to a more secure, efficient, and accessible financial industry:
- Automated Investment Advisors (Robo-Advisors): Delivering customized investment strategies based on individual risk profiles and financial objectives.
- Fraud Detection: Analyzing anomalous transaction patterns and providing real-time fraud alerts.
- Risk Management: Modeling market scenarios and proposing mitigation strategies for banks and financial institutions.
Transportation and Logistics
AI Agents are driving the transportation sector towards comprehensive automation and optimization:
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI processes sensor data to make safe driving decisions, reduce accidents, and optimize fuel efficiency.
- Intelligent Traffic Management: Predicting traffic flow, automatically adjusting traffic signals, and alleviating congestion in urban areas.
- Logistics Optimization: Calculating optimal routes and delivery times, and managing fleet operations in real-time.
Manufacturing
AI Agents enhance efficiency and reliability within the production value chain:
- Process Monitoring and Control: AI detects deviations in manufacturing processes and automatically adjusts parameters to ensure product quality.
- Predictive Maintenance: Analyzing data from machine sensors to forecast maintenance needs, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
Scientific Research
AI Agents accelerate scientific discovery by processing vast datasets and complex simulations:
- Data Analysis: Extracting patterns, trends, and correlations from millions of data points in a reduced timeframe.
- Experiment Simulation: Creating virtual models for chemical, physical, and biological experiments, saving time and costs associated with physical experimentation.
2.3 Five prominent future AI job clusters
AI Low-Code: This cluster focuses on simplifying AI development through the utilization of low-code platforms and tools. The AI Low-Code group enables the creation of AI applications without requiring extensive programming skills, empowering non-specialized organizations and individuals to implement AI rapidly and efficiently.
AI Training: This group concentrates on the training and optimization of AI models. Their responsibilities encompass data acquisition, processing, and cleansing, as well as the construction and training of models to execute complex tasks such as classification, prediction, or image recognition.
AI Automation: The AI Automation cluster centers on automating processes and tasks through the deployment of AI models. Their objective is to minimize human intervention in repetitive work, enhance efficiency, and reduce errors.
AI Research: The AI Research group is responsible for exploring novel methodologies and algorithms, identifying innovative approaches to address complex challenges within the field of AI. This group's work includes theoretical research, the development of advanced AI models, and the publication of research findings.
AI Product: The AI Product group focuses on the development and management of AI products, from defining user requirements to the design, implementation, and maintenance of AI solutions. This team collaborates closely with other departments such as software development, marketing, and customer support to ensure AI products effectively meet market needs.
3. Drivers fueling the proliferation of AI Agents

Significant Advancements in AI Technology:
Large Language Models (LLMs) and Enhanced Natural Language Understanding and Generation: The advent of Large Language Models, exemplified by GPT, has ushered in a new era in the ability to comprehend and generate natural language. These models adeptly process complex semantics, address inquiries, create content, and even produce written text and code. Leveraging vast datasets and deep learning capabilities, LLMs have achieved seamless and natural human-like communication.
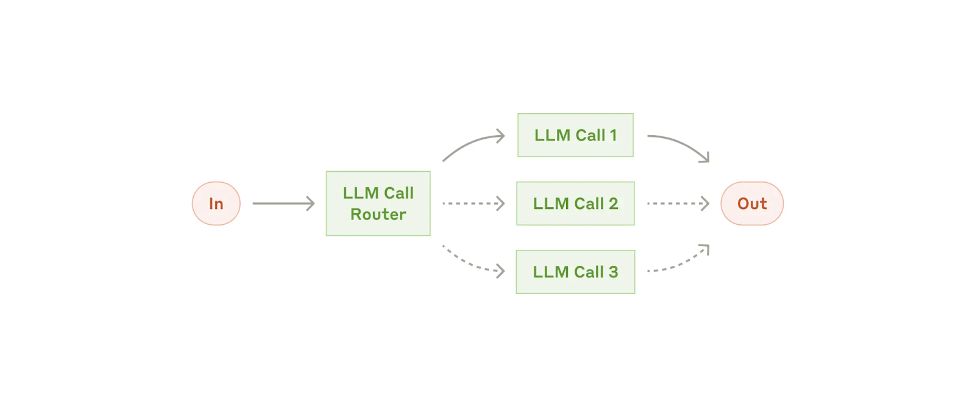
Reinforcement Learning (RL) Empowering Agents Through Interaction: Reinforcement Learning stands as a potent AI methodology wherein agents acquire knowledge through feedback from their environment or users. Moving beyond reliance on static datasets, RL agents iteratively refine their capabilities through trial and error. This empowers AI to exhibit intelligence and automate decision-making processes within intricate environments, spanning gaming, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
Computer Vision and Advanced Image Recognition and Analysis: Computer Vision represents a rapidly evolving domain within AI, enabling machines to interpret and analyze images and videos with human-like proficiency. This technology facilitates object identification, emotion analysis, and the discernment of environmental elements, finding applications across healthcare (disease diagnosis), automation, security, and entertainment (facial and image recognition in video).
Increasing Computational Power and Decreasing Costs: Progress in hardware, notably AI-centric processing units like GPUs and specialized hardware technologies, is driving significant increases in computational power while simultaneously reducing costs. This renders the deployment of sophisticated AI models both feasible and more economical, lowering cost barriers and accelerating AI adoption across diverse industries.
The Imperative for Complex Task Automation:
- Heightened pressure for efficiency and productivity within competitive business landscapes.
- A growing desire to liberate human capital from repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
- The escalating need for personalized user experiences at scale.
The Abundance of Big Data:
- Data serves as the essential "fuel" for AI Agents to learn and perform effectively.
- The proliferation of advanced data management platforms and tools.
4. Challenges and Opportunities in deploying AI Agents

Challenges:
- Ethical and Accountability Concerns: As AI Agents autonomously make decisions, determining liability in the event of errors or damages becomes complex, particularly within regulated sectors such as healthcare, finance, and legal services.
- Data Security and Privacy: AI Agents necessitate access, processing, and storage of substantial volumes of personal and sensitive data, thereby amplifying the risks of data breaches, misuse of information, and violations of user privacy.
- Lack of Explainability (Black Box Problem): Many AI Agents operate as "black boxes," making it challenging for users or organizations to comprehend the rationale and process behind their decisions, consequently eroding trust and hindering control.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Incorporating AI Agents into established legacy systems demands significant compatibility across technical infrastructure, data frameworks, and workflows, potentially incurring substantial implementation costs and timelines.
- Demand for New Skills and Talent: The proliferation of AI Agents drives a need for a workforce equipped with specialized skills in areas such as AI programming, data management, and systems analysis, necessitating continuous training and upskilling initiatives.
- Legal and Regulatory Issues: Current legal frameworks have not fully kept pace with the rapid advancement of AI, leading to ambiguities in defining legal responsibility, safety standards, intellectual property rights, and user protection.
Opportunities:
- Creation of Breakthrough Products and Services: AI Agents possess the capability to automate intricate tasks and personalize user experiences, paving the way for entirely novel products and services previously nonexistent.
- Enhanced Competitive Advantage: Organizations that adopt AI Agents can optimize processes, reduce operational costs, enhance service quality, and accelerate decision-making, thereby establishing a competitive edge within the market.
- Improved Quality of Life and Work: By automating repetitive tasks, facilitating intelligent decision support, and personalizing experiences, AI Agents enable individuals to save time, increase efficiency, and improve their daily work and personal lives.
- Addressing Complex Global Issues: With their capacity to process and analyze vast datasets, AI Agents hold the potential to contribute to the resolution of significant global challenges such as climate change, universal healthcare, personalized education, and smart city development.
5. The Future of AI Agents
Further Development and Wider Application: Driven by advancements in algorithms, data analytics, and computational power, AI Agents are poised for increasingly widespread adoption across diverse sectors, ranging from healthcare and education to finance and the creative industries.
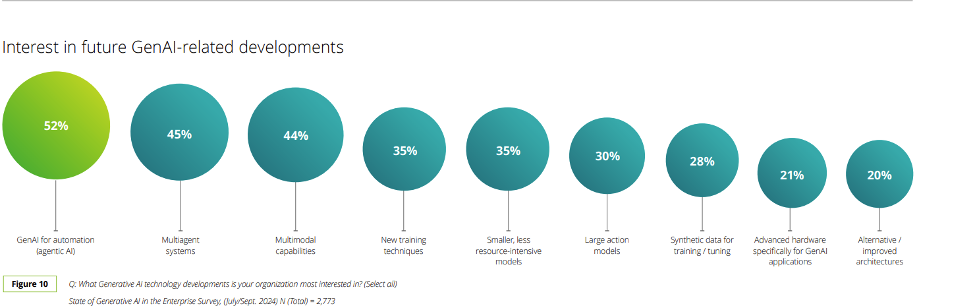
Integration with Emerging Technologies: AI Agents will not function in isolation but will be tightly integrated with other cutting-edge technologies:
- IoT (Internet of Things): Facilitating the management and coordination of billions of interconnected smart devices.
- Blockchain: Ensuring transparency, security, and decentralization in the transactions and actions executed by AI Agents.
- Metaverse: Supporting the creation of digital entities capable of interacting with and accompanying users within virtual environments.
Becoming Indispensable "Digital Assistants": In the future, individuals and organizations alike may possess their own dedicated AI Agents, acting as personalized assistants to support work processes, daily life, decision-making, healthcare management, and even providing emotional companionship.
Open Questions and Societal Considerations: The rapid advancement of AI Agents also presents critical challenges that warrant profound reflection:
- How can human oversight and control over AI be maintained effectively?
- How can we ensure that AI Agents do not exacerbate existing social inequalities?
- What ethical and legal frameworks are necessary to guarantee that AI serves the collective benefit of society?
6. Conclusion
The proliferation of AI Agents in the digital transformation era signifies not only a substantial technological advancement but also ushers in a new epoch across diverse sectors, spanning business and personal life. With their capacity to automate intricate tasks, learn, and adapt over time, AI Agents are becoming indispensable "digital assistants," enhancing operational efficiency, personalizing user experiences, and unlocking new, high-potential business models. Contact us for consultations and complimentary resources on the latest emerging technology trends.